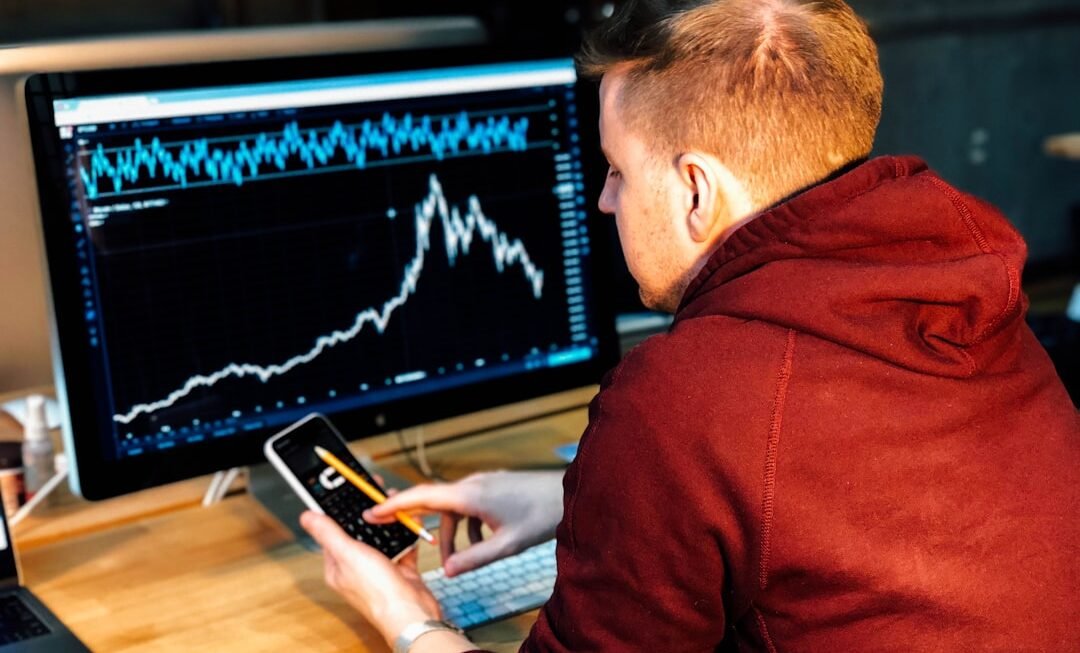
As I delve into the realm of quantum computing, I find myself captivated by its fundamental principles, which diverge significantly from classical computing. At its core, quantum computing harnesses the peculiarities of quantum mechanics, particularly the behavior of subatomic particles. Unlike classical bits, which exist in a state of either 0 or 1, quantum bits, or qubits, can exist in multiple states simultaneously due to a phenomenon known as superposition.
This unique property allows quantum computers to process vast amounts of information at unprecedented speeds. Moreover, entanglement is another cornerstone of quantum mechanics that plays a crucial role in quantum computing. When qubits become entangled, the state of one qubit becomes intrinsically linked to the state of another, regardless of the distance separating them.
This interconnectedness enables quantum computers to perform complex calculations that would be infeasible for classical computers. As I explore these concepts further, I realize that the potential applications of quantum computing extend far beyond theoretical physics; they promise to revolutionize various fields, including finance, cryptography, and artificial intelligence.
Classical Computing: The Linear Approach
Classical computers have been the driving force behind technological advancements for decades. They operate on binary logic, processing information in a linear fashion. While they excel at tasks that require straightforward calculations and data manipulation, they struggle with problems that involve vast datasets or complex variables.
Quantum Computing: Tackling Complexity with Ease
In contrast, quantum computers leverage the principles of superposition and entanglement to tackle complex challenges more efficiently. The difference in processing power is staggering. While a classical computer might take years to solve certain problems, a quantum computer could potentially arrive at a solution in mere seconds.
The Power of Parallelism
This capability stems from the parallelism inherent in quantum computing; multiple calculations can occur simultaneously due to the qubits’ ability to exist in multiple states. As I reflect on this distinction, I recognize that the implications for industries reliant on data analysis and complex modeling are profound.
Redefining Problem-Solving Across Industries
The shift from classical to quantum computing could redefine how we approach problem-solving across various sectors. The potential impact is vast, and I am excited to explore the possibilities that quantum computing has to offer.
Key Takeaways
- Quantum computing utilizes quantum mechanics to process and store data in quantum bits (qubits) which can exist in multiple states at once, allowing for faster and more complex calculations.
- Quantum computing has the potential to outperform classical computing in solving certain types of problems, such as factoring large numbers and simulating quantum systems.
- Quantum computing’s impact on financial trading includes the potential to optimize portfolio management, risk assessment, and algorithmic trading strategies.
- Advantages of quantum computing in financial trading include the ability to process large amounts of data and perform complex calculations at a much faster rate than classical computers.
- Challenges and limitations of quantum computing in financial trading include the need for error correction, the high cost of development and implementation, and the limited availability of quantum computing resources.
Quantum Computing’s Impact on Financial Trading
As I consider the implications of quantum computing for financial trading, I am struck by the transformative potential it holds for the industry. Financial markets are characterized by their complexity and volatility, with countless variables influencing asset prices. Traditional trading algorithms often struggle to keep pace with these dynamics, leading to missed opportunities and suboptimal decision-making.
Quantum computing offers a new paradigm that could enhance trading strategies and risk management. One of the most significant impacts of quantum computing on financial trading lies in its ability to analyze vast datasets in real-time. With the power to process information at lightning speed, quantum computers can identify patterns and correlations that would remain hidden to classical systems.
This capability could lead to more accurate predictions of market movements and improved trading strategies. As I contemplate this potential, I envision a future where traders can make informed decisions based on comprehensive analyses rather than relying solely on historical data or intuition.
Advantages of Quantum Computing in Financial Trading
The advantages of integrating quantum computing into financial trading are manifold. One of the most compelling benefits is the enhanced speed and efficiency with which quantum computers can execute trades. In an environment where milliseconds can mean the difference between profit and loss, the ability to process information rapidly is invaluable.
Quantum algorithms can optimize trading strategies by evaluating multiple scenarios simultaneously, allowing traders to capitalize on fleeting market opportunities. Additionally, quantum computing can significantly improve risk assessment and management in financial trading. By simulating various market conditions and stress-testing portfolios with unprecedented accuracy, traders can better understand potential risks and devise strategies to mitigate them.
This level of insight could lead to more resilient trading practices and ultimately contribute to greater market stability. As I reflect on these advantages, I am excited about the prospect of a more efficient and informed trading landscape driven by quantum technology.
Challenges and Limitations of Quantum Computing in Financial Trading
Despite its promise, I recognize that quantum computing also faces significant challenges and limitations in the context of financial trading. One major hurdle is the current state of quantum hardware and software development. While progress has been made, many quantum computers remain in their infancy, grappling with issues such as qubit coherence and error rates.
These technical limitations can hinder their practical application in real-world trading scenarios. Moreover, there is a steep learning curve associated with adopting quantum computing technologies within financial institutions. Many professionals in finance may lack the necessary expertise to understand and implement quantum algorithms effectively.
This gap in knowledge could slow down the integration of quantum computing into existing trading systems and processes. As I consider these challenges, I realize that overcoming them will require collaboration between technologists and finance professionals to bridge the divide and unlock the full potential of quantum computing.
Quantum Computing Algorithms for Financial Trading
As I delve deeper into the world of quantum computing algorithms tailored for financial trading, I am fascinated by the innovative approaches being developed to harness this technology effectively. One prominent algorithm is the Quantum Approximate Optimization Algorithm (QAOA), which is designed to solve combinatorial optimization problems commonly encountered in finance. By leveraging quantum superposition and entanglement, QAOA can explore multiple solutions simultaneously, identifying optimal trading strategies more efficiently than classical counterparts.
Another noteworthy algorithm is Grover’s Search Algorithm, which offers a quadratic speedup for unstructured search problems. In financial trading, this could translate into faster identification of profitable trades or investment opportunities within large datasets. As I explore these algorithms further, I am encouraged by their potential to revolutionize how traders approach decision-making and strategy formulation.
Future Prospects of Quantum Computing in Financial Trading
Looking ahead, I am optimistic about the future prospects of quantum computing in financial trading. As advancements in quantum hardware continue to unfold, we may witness a gradual shift toward more widespread adoption within financial institutions. The potential for enhanced predictive analytics and risk management capabilities could lead to a new era of data-driven decision-making in trading.
Moreover, as collaboration between technologists and finance professionals deepens, we may see the development of user-friendly tools that democratize access to quantum computing capabilities. This accessibility could empower a broader range of traders and investors to leverage quantum technology in their strategies, ultimately reshaping the competitive landscape of financial markets. As I envision this future, I am excited about the possibilities that lie ahead for both quantum computing and financial trading.
Ethical and Regulatory Considerations for Quantum Computing in Financial Trading
As I contemplate the integration of quantum computing into financial trading, I cannot overlook the ethical and regulatory considerations that accompany this technological shift. The unprecedented speed and power of quantum computers raise questions about fairness and transparency in financial markets. If only a select few institutions possess access to advanced quantum algorithms, it could create an uneven playing field that undermines market integrity.
Furthermore, regulatory frameworks will need to evolve to address the unique challenges posed by quantum computing. Issues such as data privacy, algorithmic accountability, and market manipulation must be carefully considered as regulators seek to ensure a level playing field for all market participants. As I reflect on these ethical dilemmas, I recognize that fostering collaboration between industry stakeholders and regulatory bodies will be essential in navigating this complex landscape.
In conclusion, my exploration of quantum computing reveals its transformative potential for financial trading while also highlighting the challenges and ethical considerations that must be addressed. As this technology continues to evolve, I am excited about its implications for enhancing decision-making processes and reshaping the future of finance. The journey ahead may be fraught with obstacles, but the promise of a more efficient and equitable trading environment makes it a pursuit worth undertaking.